If you are building a PC, you might want to know whether a PWM fan or a DC fan is the best choice for your CPU and Chassis. You may also be dissatisfied with your current fans and want to know whether the other type would have been better.
In short, a PWM fan is generally better than its counterpart in all regards but the difference is not that significant for the latest fans. The fan dimensions as well as the models end up mattering more. Some manufacturers have even created DC fans that are better than most PWM fans.
In my computer setup, I use a PWM fan for my CPU and four DC fans (3 in front and one in back) for the chassis.
What is a DC Fan?
A (Direct Current) DC computer fan uses a connector with three pins, which include:
- Ground pin
- 12V power supply pin
- Tachometer pin

The tachometer pin output is connected to a hall sensor on the fan circuit that uses the magnetic field to check the RPM and whether the fan has stopped. This pin provides this information to the motherboard. The hall sensor also allows the motor to rotate properly.
The 12V power supply provides the voltage to the fan motor. While controlling fan speed on a DC fan, the motherboard provides 12V to this pin for full speed or a less value for a lower fan speed.
So the motherboard needs to directly decrease/increase the voltage to a DC fan to control its speed.
What is a PWM Fan?
A (Pulse Width Modulation) PWM fan contains more circuit elements like a separate logic control circuit, oscillators, and so on. It uses a 4-pin connector and the pins are:
- Ground pin
- 12V power supply pin
- Tachometer pin
- PWM pin

The Tachometer pin outputs the fan information to the motherboard similar to the DC pin. However, everything else works in a different way.
The power supply pin always provides the full 12V to the fan. The hall sensor works in conjunction with the PWM signal and other circuit elements to modulate the fan speed.
The PWM signal turns the fan on and off rapidly in particular intervals. This duty cycle (ratio of time when the PWM signal or the fan is ON to the time when the fan is OFF) is the main way to control the speed.
Essentially, if a 12V fan has a duty cycle of 50% (is ON only 50% of time), it uses an average voltage of 6V for the duration. So its speed gets lowered to what the speed would be if the motherboard provided 6V DC to the fan.
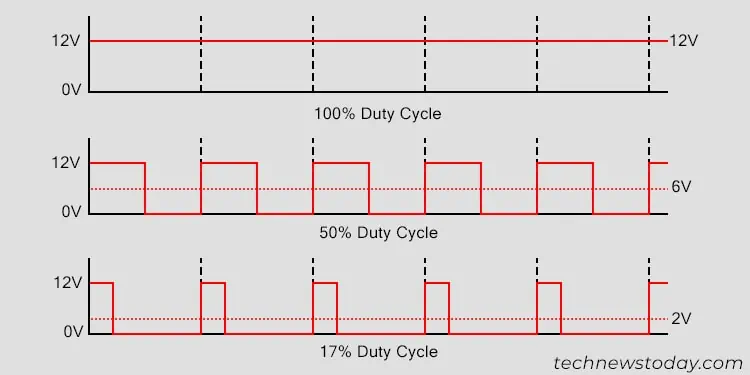
Differences Between PWM and DC Fans
PWM and DC fans work using different technologies. So even if these fans with same specs provide similar airflow, other parameters like speed control, noise, power consumption, and so on, have some differences.
Speed Control and Minimum Speed Possible
The PWM fans generally provide much better speed control than DC fans since it is relatively easier to control the duty cycle than the input voltage. However, the latest motherboards have started providing good control even for DC fans. What does matter nowadays is the minimum possible speed for the fans.
While lowering the input voltage for the fans decreases its motor speed, each motor requires a minimum voltage to operate, or else it will stall. For DC fans, it means that there’s a limit to how much the voltage control can lower the fan speed.
The motors on PWM fans get full voltage in each duty cycle when the fans are ON. So their minimum possible speed is much lower compared to DC fans. However, it is still impossible to reach near zero speed as the motor won’t run if the duty cycle is too low.
Noise
Nowadays, how noisy the fans are actually depends more on the dimensions and manufacturing technology than the control mode. With similar materials, dimensions and manufacturing technology, PWM fans should be quieter overall as they can reach lower speeds than DC fans.
On the other hand, depending on your PC usage, the fan may need to increase and decrease its speed quite often. So for PWM fans, it translates to frequent fluctuation in the noise. A DC fan will provide a consistent noise, so it might be easier to get used to.
Also, the noisiest fan is always going to be the CPU fan. So if you want a quieter PC experience, it’s always better to install bigger and more case fans, regardless of whether they use DC or PWM. This way, the CPU fan does not need to work harder to maintain the CPU temperature.
Power Usage and Sustainability
PWM fans are more power efficient specifically because they operate at lower speeds overall and also run for less time compared to DC fans. Also, since PWM fans only actually rotate a fraction of the time, they don’t wear out as quickly as DC fans.
Cost
In general, PWM fans cost more to manufacture than DC fans since they need additional circuit components. Consequently, they will cost slightly more in their retail values as well.
However, the cost difference is very minimal, especially if you use RGB fans as the RGB LEDs and controllers will add considerable overhead to the cost.
Regardless, if you want to use many case fans to minimize the noise and want to save your budget whenever possible, you can go for the DC fans.
Compatibility
Most modern motherboards have 4-pin fan headers where you can use either PWM or DC fans.
However, since PWM fans are newer technologies than 3-pin DC fans, many older motherboard models only have 3-pin headers. Connecting a PWM fan to such headers will make the PWM pin useless and you will only be running the fan as a DC fan.
Which Fan is Better for My PC?

If we consider all the differences between the PWM and DC fans, PWM fans do have a slight edge over DC fans. But the difference is not that much in the current scenario.
In conclusion, if you only have 3-pin fan headers on the motherboard, use a DC fan. If you have 4-pin headers, it is preferable to go for a PWM one, but a DC fan is also fine. What does matter is that you use more than one chassis fan, especially for beefy rigs, for the best airflow and the least noise.
Also, speed control is not much of an issue for chassis fans as compared to CPU fans. So it is generally recommended to use a PWM fan as the CPU fan. However, you can set any type of fan as the chassis or case fans.
