A hypervisor runs on a physical host and partitions the host’s resources among various virtual environments. There are two types of hypervisors.
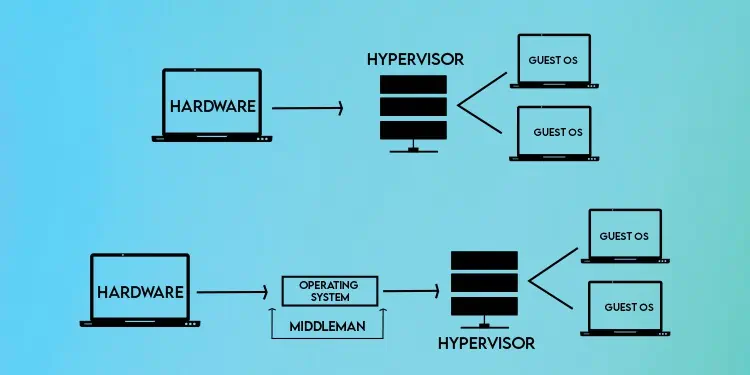
Type 1, or bare-metal hypervisors, are installed directly on top of the physical host or server. Type 2, or hosted hypervisors, instead have an OS layer between it and the physical host.
The way Type 1 vs Type 2 hypervisors perform virtualization, the resource access and allocation, performance, and other factors differ quite a lot.
As there are certain pros and cons to both types, picking the right one for your use-cases can be difficult, but this article should give you a better understanding to that end.
What’s a Type 1 Hypervisor?
As shown in the figure, Type 1 Hypervisors run on top of the physical host and interact directly with the hardware, with no OS in between, as Type 1 itself acts as an OS. Thanks to this, Type 1 Hypervisors have better performance, efficiency, and security.
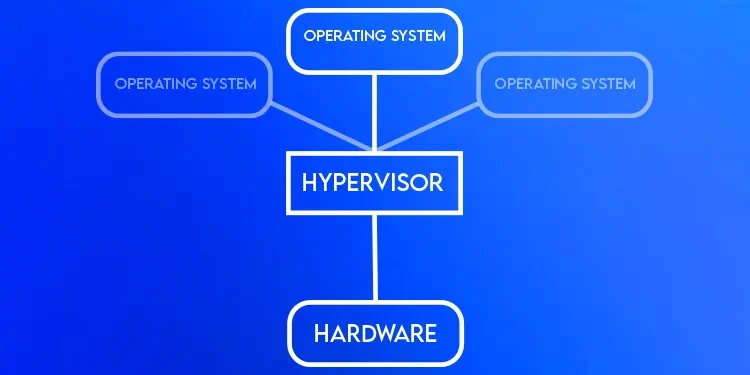
However, they are also more complicated to set up, use, and debug for the same reason. After all, every Type 1 is different from the other in terms of working mechanisms, meaning more hours are required to familiarize yourself with the setup and system.
Additionally, devices required to run Type 1 Hypervisors must be specifically designed for virtualization, rendering them useless for any other purpose.
Some popular Type 1 vendors include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Citrix XenServer.
- Direct hardware access
- Efficient resource allocation
- Better performance and security
- Highly scalable
- Difficult to set up and maintain
- Steep licensing costs
What’s a Type 2 Hypervisor?
On the other hand, Type 2 Hypervisors run on top of an OS layer. This makes them more prone to vulnerabilities, and the performance isn’t as good either compared to Type 1. But on the contrary, they are much easier to set up, use and troubleshoot.
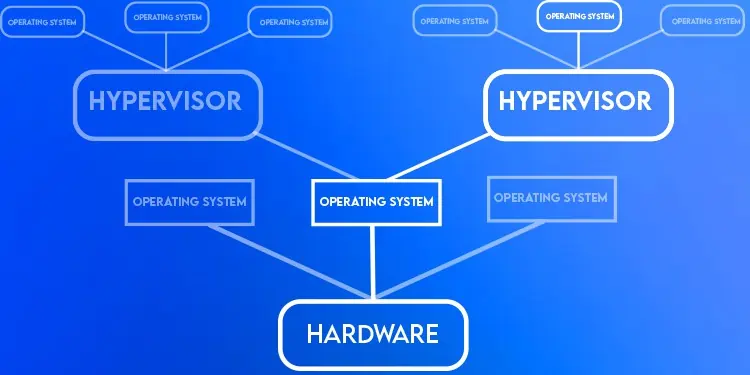
Some popular Type 2 vendors include VMware Workstation Player, Oracle VM VirtualBox, and QEMU.
- Both affordable and completely free options available
- Easy to set up and maintain
- Performance and security isn’t as great
- Resource allocation is inefficient
- Limited scalability
KVM is a bit more complicated. KVM lets the Linux kernel function as a Type 1 hypervisor, but simultaneously, the overall system is categorized as a Type 2 hypervisor. The VMs themselves are implemented as normal Linux processes.
How Are These Two Different?
Here are the main differences between Type 1 vs Type 2 Hypervisors:
Virtualization Level
Type 1 Hypervisors perform virtualization at the hardware level. Usually, Ring 0 is the protection level with the most privileges as it offers direct hardware access.
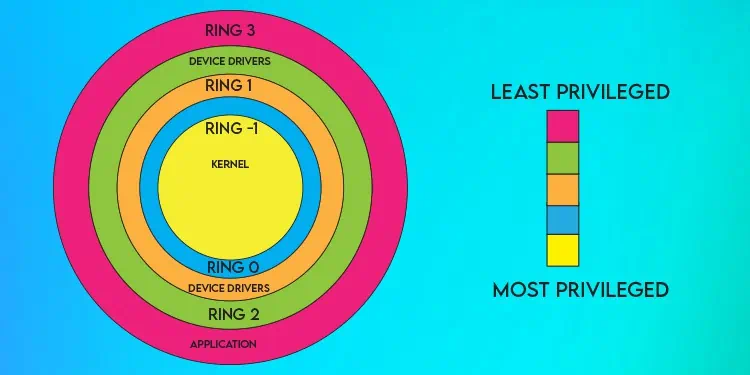
But Intel VT-x and AMD-V insert a new ring underneath it called Ring -1, which allows the guest OS to perform Ring 0 operations without compromising anything else. This essentially means that Type 1 Hypervisors are faster and more efficient, and hardware features are directly accessible.
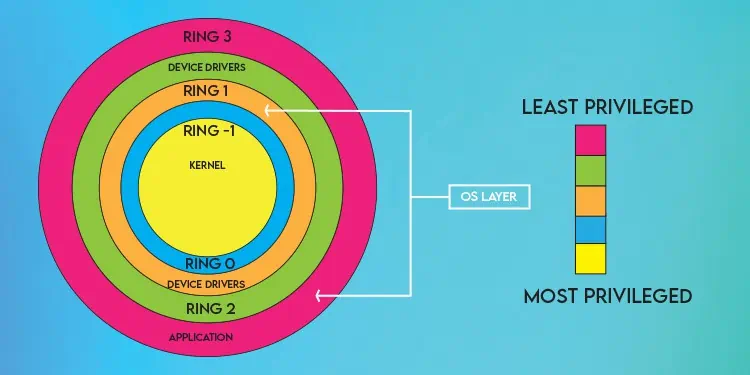
On the other hand, Type 2 Hypervisors perform virtualization at the operating system level. There’s an OS layer between the hypervisor and physical host, meaning the hypervisor doesn’t have direct hardware access.
Instead, the kernel creates isolated user spaces where the guest OS runs, similar to any other application or process. This means Type 2 hypervisors run at Ring 1 or higher.
Resource Allocation
Type 1 Hypervisors assign resources dynamically. For instance, let’s say you have a server with 64 GBs of memory and 6 virtual servers running on it. If you want to assign 16 GBs or more to each server, you can safely do so even though the total would technically come out higher than what should be possible.
In a real-world scenario, it’s highly unlikely that all the virtual servers will max out their memory usage simultaneously.
In the case of Type 2 hypervisors, the virtual servers occupy all of the assigned resources even if they don’t actually need them.
Performance
As stated, Type 1 hypervisors run directly on top of the host with no middleman, which translates into better performance.
Contrasting this, Type 2 hypervisors run on top of an OS layer. The guest OS is dependent on the host OS for access to resources, which results in higher latency.
Security
Although extremely rare, there’s always the possibility of hyperjacking, regardless of the hypervisor type. But barring this minor possibility, Type 1 Hypervisors are very secure.
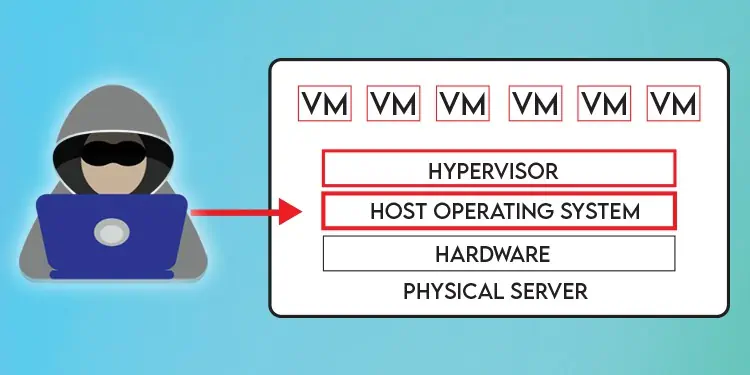
Type 2 hypervisors, on the other hand, are not as reliable. Any problems with the underlying host OS, from malware and hacking to crashes, can affect the performance of the VMs.
Scalability
Considering the various factors we’ve detailed so far, from resource allocation and efficiency to performance and security, it should come as no surprise that Type 1 hypervisors are vastly more popular in enterprise environments.
Type 2 hypervisors, which have to rely on the underlying OS, have comparatively limited scalability. They are better suited for personal use or certain environments where devs need to test and use various operating systems.
Similarities Between Type 1 & Type 2 Hypervisors
The prime similarity between Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors is that they can both make use of hardware-assisted virtualization. Compared to software virtualization, where the hypervisor handles everything independently, modern processors can assist hypervisors with virtualization to maximize performance and minimize overhead.
How Are Type 1 Hypervisors Better?
As we’ve detailed in the sections above, Type 1 Hypervisors are better in terms of most metrics, from security, performance, and scalability, to resource access and allocation.
As such, they are commonly used in large server environments such as data centers or enterprises.
Should You Use Type 2 Hypervisors?
While Type 1 Hypervisors are better if we go by the raw specs, Type 2 Hypervisors are better options in certain scenarios.
For starters, Type 2 Hypervisors are simpler to set up and use. They are also typically affordable or entirely free. This is not the case with Type 1 Hypervisors, where the licensing costs are quite high, and in the cases of free options, the functionality is limited.
This makes Type 2 Hypervisors better suited for personal use. After all, it doesn’t make sense to purchase expensive Type 1 licenses just to set up a couple of operating systems in your home lab.
The same reasoning is true for certain professional environments as well. Tech professionals often need access to different operating systems for testing on different platforms. In such cases, Type 2 Hypervisors are a popular solution.
Final Verdict – Type 1 Vs Type 2 Hypervisor
Type 1 hypervisors can seem better on paper, but there are real-world applications for both hypervisor types. The right one for you will depend on your specific needs and use cases, as we’ve detailed in this article. Finally, to recap, here are the key differences between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisors:
| Type 1 | Type 2 | |
| Virtualization Level | Virtualization occurs on the hardware level (Ring 0). | Virtualization occurs on the OS level (Ring 1 or higher). |
| Resource Access | Direct access to hardware features. | Requests have to be directed to the host OS first. |
| Resource Allocation | Supports dynamic resource allocation. | Resource allocation is not as efficient. |
| Performance | Better performance. | Comparatively worse performance. |
| Security | More secure. | Not as secure. |
| Scalability | Better scalability. | Not as scalable. |
| Examples | VMware ESXi Microsoft Hyper-V Citrix XenServer | VMware Workstation Player Oracle VirtualBox QEMU |

