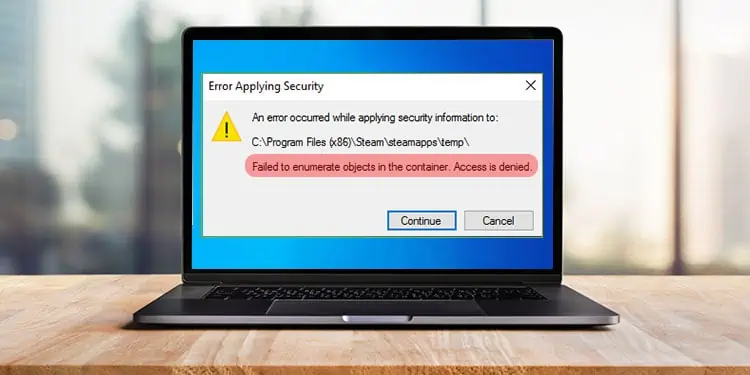
Windows provides a security mechanism for files and folders that lets you define user accounts to access it. Sometimes, when trying to alter the permission settings for a folder, you might have come across the error message Failed to enumerate objects in the container.
Mostly, this error occurs when you don’t have ownership over the folders or say you don’t have administrator privileges. You will also encounter the error if any system files are corrupted. But don’t worry! This problem is solve able and has some simple fixes.
In this article, you will learn a few proven ways to fix this error in Windows.
Fix: Failed to enumerate objects in the container
Since giving access to your files and folders deals with privacy, you should sort out this problem as soon as possible. You can simply perform minor tweaks in your folder settings and easily sort out the issue.
Here, we have compiled a list of 5 fixes you can apply when facing this error. Let’s dive straight into them.
Take Over Ownership and Change Permissions
The first thing you can do when you face this error is change the file or folder ownership manually. This is the most recommended fix by Microsoft, and many users reported that they sorted out the issue after applying this fix.
Follow these steps to change the file ownership manually:
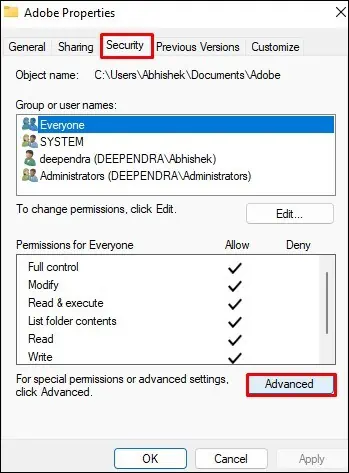
- Navigate to the files or folder whose permissions you want to change. Right-click over it and select Properties from the context menu.
- Jump to Security tab and then click Advanced.

- Click Change next to the Owner name.
- In the next popup, type the account name in the text field under Enter the object name to select and click Check Names. Your account name will appear with an underline if it is found. Else click the Advanced button and locate your username.

- Click OK button.
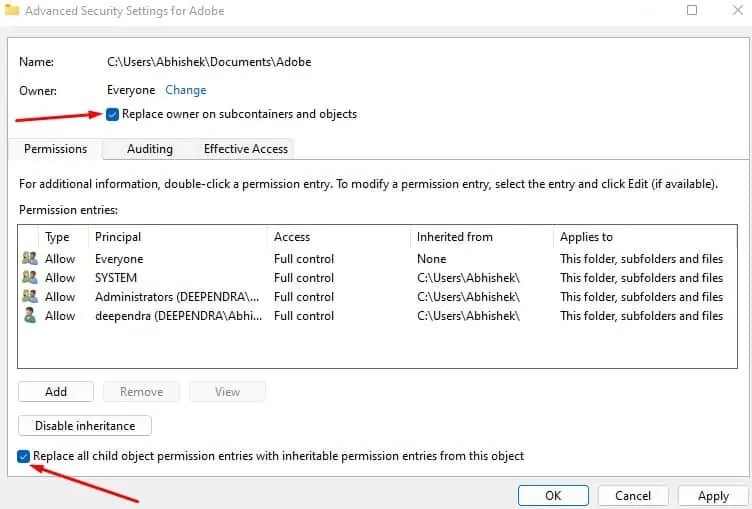
- In the next window, check both options: Replace owner on sub containers and objects and Replace all child object permission entries with inheritable permission entries from this object.

- Click Apply button and then confirm the changes in the confirmation dialog box.
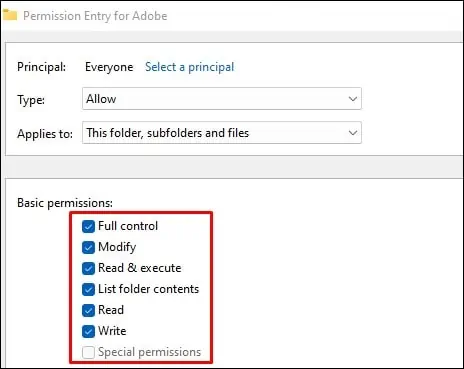
- Click Add button in the Advanced security settings window and click Select a Principal in the Permission Entry window.
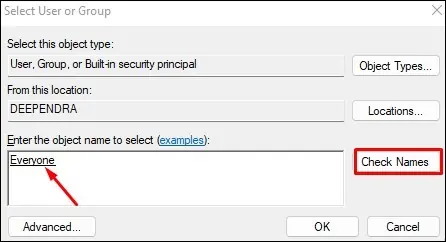
- In the Select User or Group popup, type Everyone in Enter the object name to select text field and click Check Names.
- Click OK and then check the Full Control option under Basic permissions.

- Click OK button on every window you have opened to save the changes and exit.
- Now try to set the permissions for the desired file. You should not encounter the problem.
Use Commands to Grant Permissions
The first method should work like a charm but if you still face the error while setting the permissions, try an elevated command prompt method to grant the permissions. Here’s how:
- In the Windows search box, type Command Prompt.
- Right-click over the top result and select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes in the UAC popup.
- Copy and paste the following commands serially.
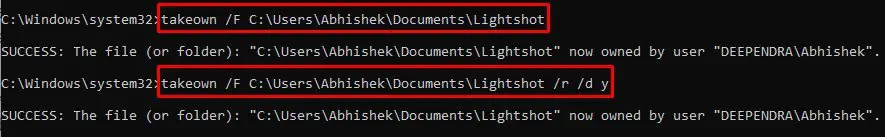
takeown /F X:\Full_Path_to_Foldertakeown /F X:\Full_Path_to_Folder /r /d y
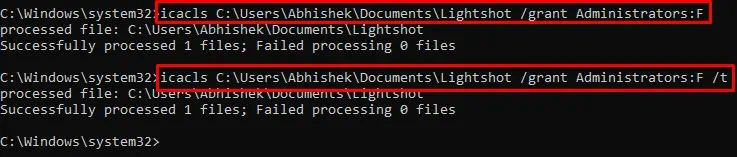
icacls X:\Full_Path_to_Folder /grant Administrators:Ficacls X:\Full_Path_to_Folder /grant Administrators:F /t
- Consider pressing the Enter key after each command and replacing
X:\Full_Path_to_Folderwith the file/folder location whose permissions you are trying to change. Full path looks like:C:\Users\Deepen\Documents\Lightshot - After you execute the commands successfully, try changing the permissions again and see if the issue persists.
Run CHKDSK, SFC and DISM Commands
CHKDSK mainly deals with checking and fixing the issues in the file system. It checks for errors on your hard drive and repairs them. Try running it if the above two methods do not solve your problem. Running the CHKDSK command can help identify and fix issues with corrupted file systems and solve the error. Follow these steps to run it:
- In the Windows search box, type Command Prompt, right-click over it, and select Run as administrator.
- Type
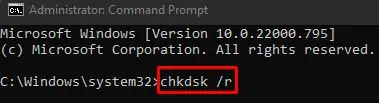
chkdsk /rand hit Enter.
- Type
chkdsk /fand hit Enter. - The disk checking process will start after this. Or you may see Chkdsk cannot run because the volume is in use by another process. Would you like to schedule this volume to be checked the next time the system restarts? (Y/N) message. If you see this message, press the “Y” key on your keyboard and hit Enter.
- Restart your computer to run the disk checking process.
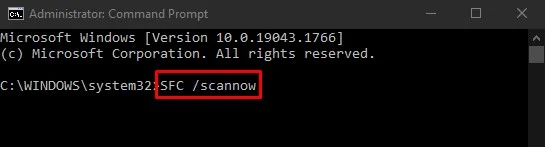
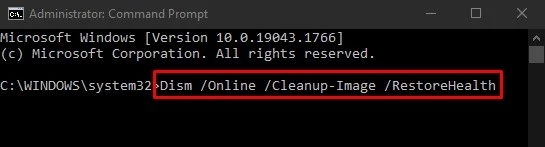
You can also use SFC and DISM commands since they also deal with repairing the corrupted system files. Run the SFC command at first and see if the issue persists while changing permissions. If it does, run the DISM command afterward. Else no need to run the DISM command. Follow these steps:
- In the Command Prompt window, type
SFC /scannowand hit Enter key to run SFC tool.
- Type
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealthand press Enter key to run the DISM tool.
Disable UAC Notifications
User Account Control (UAC) is a kind of security mechanism built-in into Windows. It prompts an administrator for confirmation before any program tries to make changes to the computer. However, the UAC feature sometimes may be the culprit behind the failed to enumerate objects error.
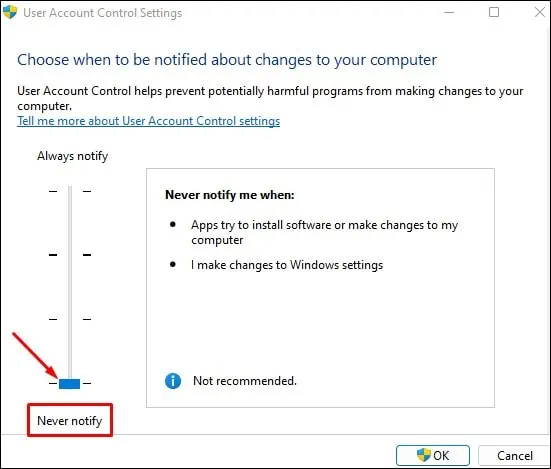
If you disable this, you will not be asked for any confirmations when you try changing the folder permissions. And probably, you may be able to change permissions without any issue. Here’s how to disable the UAC notifications:
- Hit Windows + S key on your keyboard, type Change User Account Control Settings, and open it.
- In the new window that opens, you will see a slider between Always notify and Never notify. Slide it to Never notify and click the OK button.

- Click Yes in the UAC dialog box.
Note: Since UAC control is useful in notifying you about the changes that will be made to your PC, disabling it permanently is not recommended. You must re-enable it if you can set the folder permissions successfully.
Boot into Safe Mode
Booting your computer in safe mode loads only the elementary programs and drivers set required for booting the PC. If any other applications or programs are causing the error, you will easily figure it out once you boot in safe mode. Follow these steps to boot into safe mode:
- Right-click the Start button and select Run from the list of options.
- Type
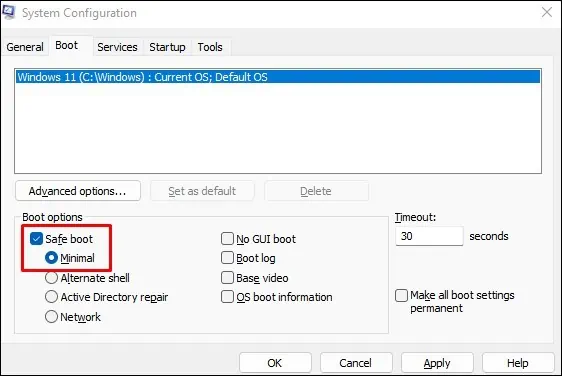
msconfigin the text field and hit Enter to open the System Configuration application. - Navigate to the Boot tab and check the box next to Safe boot under Boot options.
- Select Minimal and then click Apply > OK.

- Restart your computer to boot into safe mode.
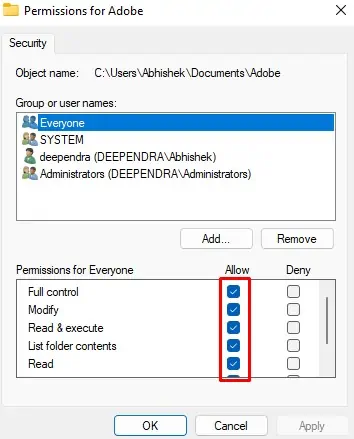
How to Change File and Folder Permission in Windows?
You can specify which users to give permissions to a particular folder in Windows. You can further define what actions they can perform like Full Control, Modify, or just Read-only. Follow these steps to change the file and folder permission in Windows:
- Locate the folder whose permissions you want to change. Right-click over it and select Properties from the context menu.
- Click the Security tab. You will see two sections within it. In the Group or user names section, you will see the accounts that exist in the system. In the Permissions section, you will see what that particular account is permitted to do.
- Select the user account whose permissions you want to change from the upper section and click the Edit button.

- In the next popup window, check the box beside the permissions type and click the OK button.