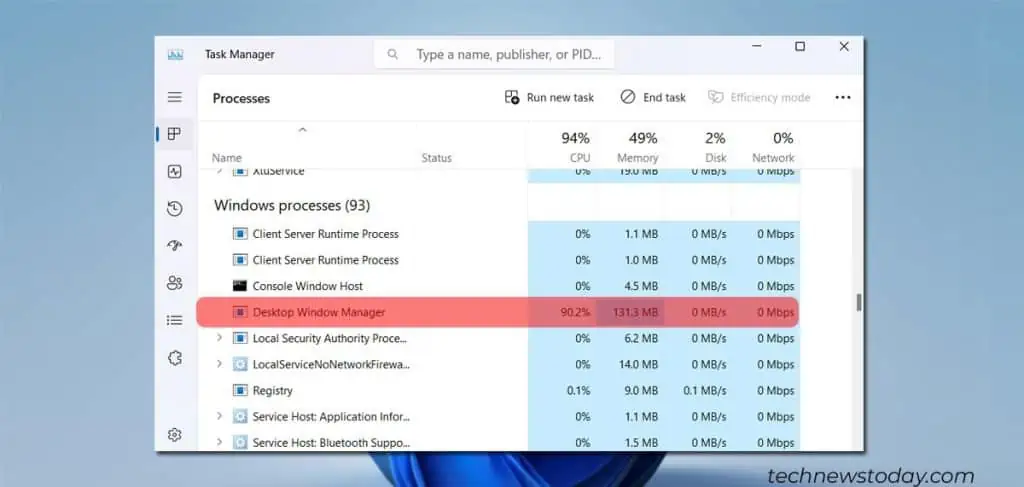
Windows Desktop Manager is the utility responsible for many of the visual effects you see on Windows. It is almost always running and requires some system resources. However, it shouldn’t be the dominant process consuming your CPU resources, making it difficult to run other processes.
This issue often arises when your system relies on the CPU rather than the GPU for generating visual effects, especially if you have a mediocre CPU that is incapable of handling these tasks.
However, some people also report that the issue is related to specific drivers. If you’re seeing a lot of CPU usage and using an old driver, it could be the culprit.
It can take time to pinpoint the cause of high system utilization for Desktop Window Manager. So, the best way to approach fixing it is to go through a list of solutions to see which one works for you.
Change Desktop Settings
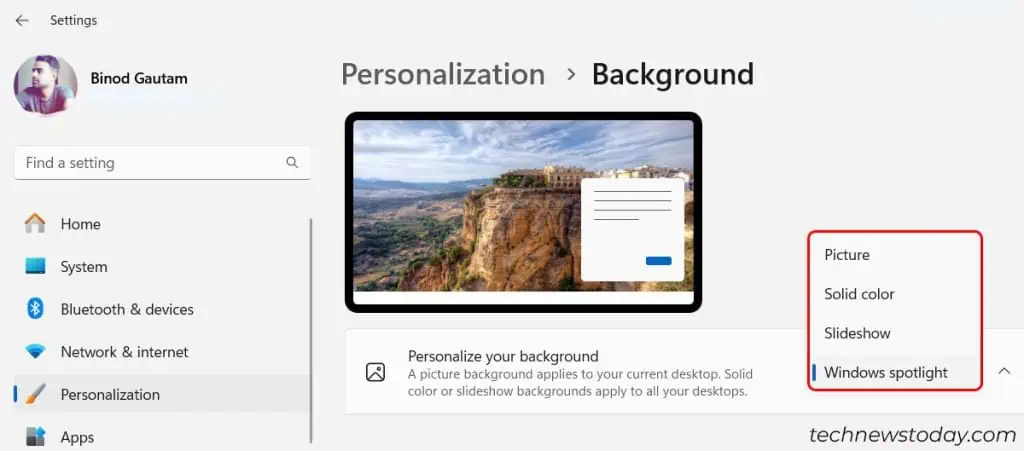
Since Desktop Window Manager deals with things like your desktop background and theme, changing it might help. It’s especially likely to work if you use custom themes or animated desktops. Displaying these might take a bit of a toll on your system.
- Open Settings.
- Select Personalization > Background.
- Replace the current settings with something that would seem easier on your system. For example, if your background is a slideshow, change it to a static image.
- Continue going through the list on the left sidebar. Try changing to the Windows default sounds and the default cursor. Removing complex customization will give you the best shot at lowering the system’s resource utilization.
Change Priority for DWM Process
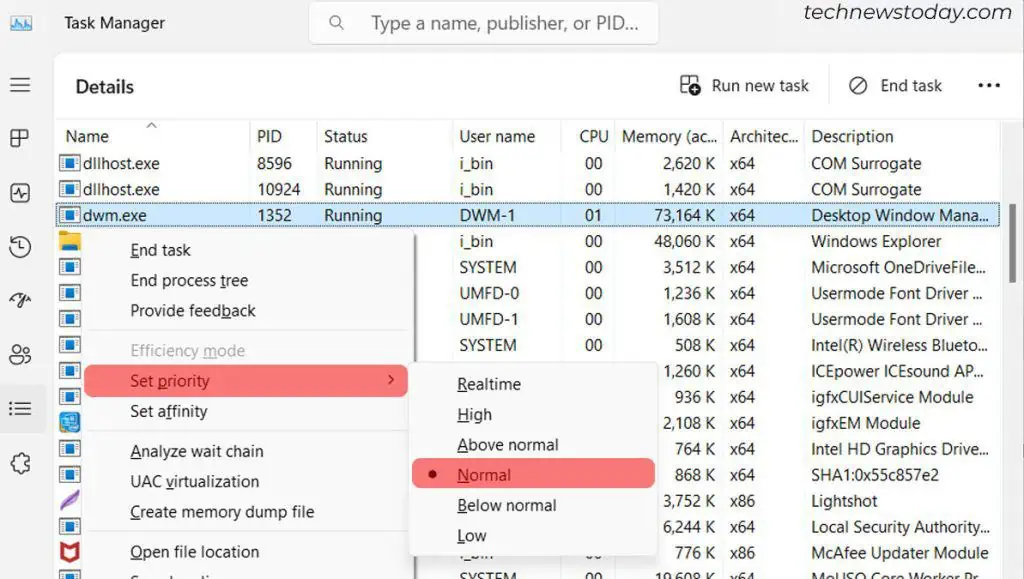
Windows allows you to run several Windows processes with different priorities. If you have the dwm.exe process set with high priority, it might consume high CPU resources.
In such a case, it is best to set the priority to normal. Doing so operates the process at a standard priority level and helps reduce CPU usage.
- Open Task Manager.
- Click on the Details tab.
- Right-click on the
dwm.exeprocess and click on Set Priority > Normal. - On the next prompt, click on Change Priority.
Adjust for Best Performance
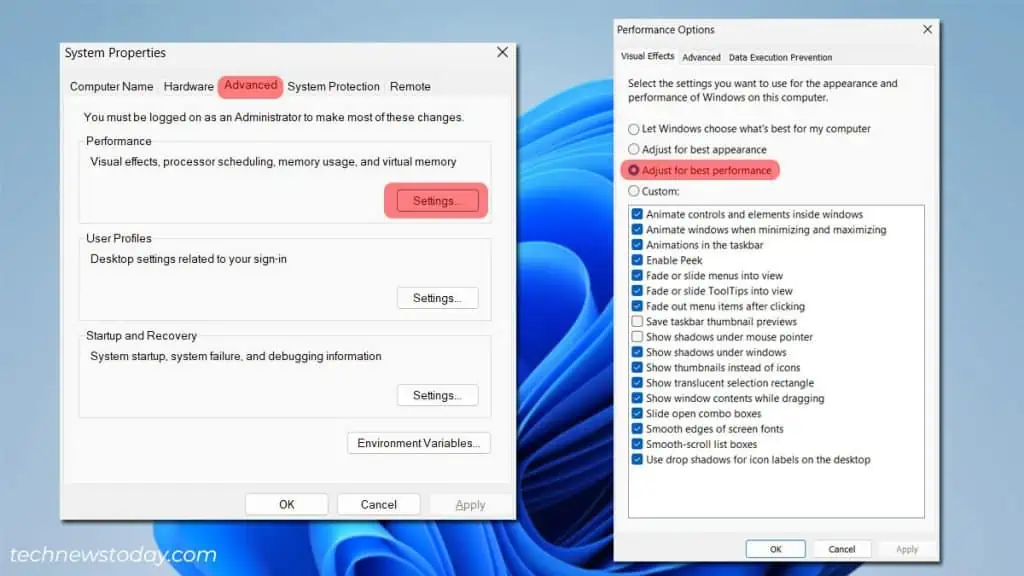
Windows offers a lot of visual effects to make the UI look more interesting and engaging. However, these might increase the amount of resources Windows uses to run dwm.exe. Turning them off can help you conserve resources.
- Open Run.
- Type
sysdm.cpland press OK. - Choose the Advanced tab.
- Click Settings under Performance.
- Select Adjust for Best Performance under the Visual Effects tab.
- Click Apply > OK.
You may notice some differences in how things look in your system, but it may also help it work better.
Update Windows and Graphic Drivers
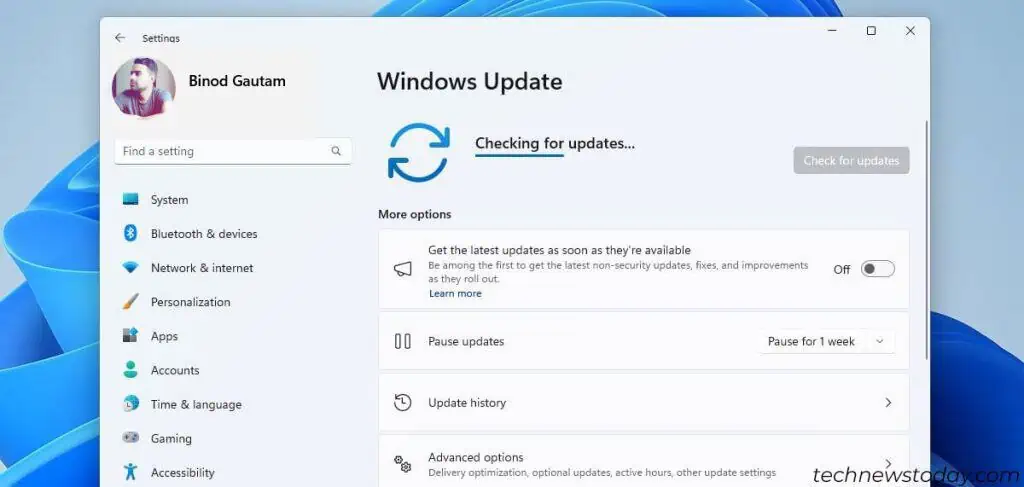
Do it now if you don’t regularly update your operating system. Fixes in these updates can address problems like the Desktop Window Manager’s high resource utilization.
- Open Settings.
- Click on Windows Update.
- Check for updates and then let the system download and install them. You may have to restart your computer to complete the process.
The issue with Desktop Window Manager and high CPU usage may also arise if you have outdated graphics drivers. So, it’s always the best idea to keep your graphics driver updated.
You can also download drivers from the manufacturer’s website and manually update your NVIDIA and AMD drivers.
Once you’re done with the process, restart your computer and check on the Desktop Window Manager resource utilization.
Run a Virus Scan
An unwanted program may cause problems on your computer. Sometimes the signs of a virus or malware are subtle issues like high resource utilization. Luckily, Windows has its own antivirus software to help you keep your computer secure.
- Open Settings.
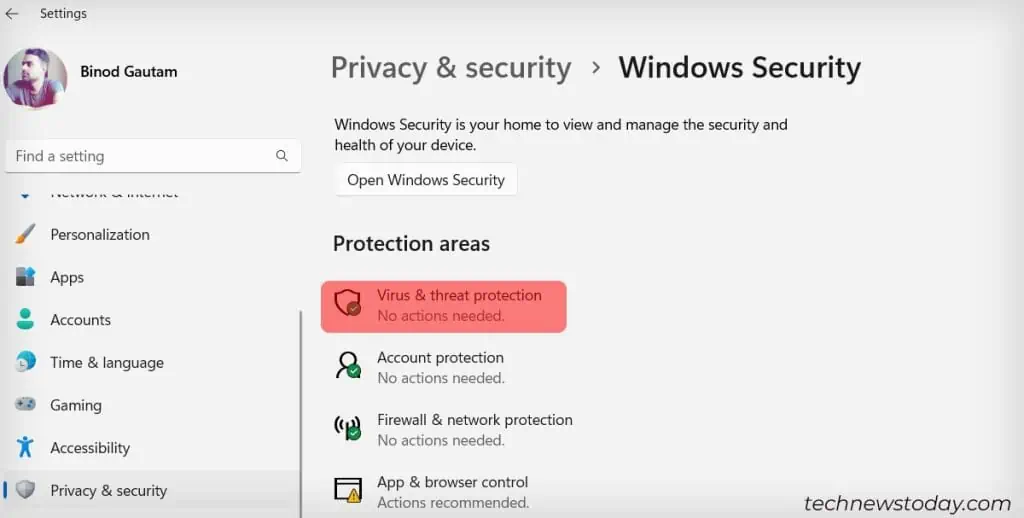
- Choose Privacy & Security.
- Select Windows Security.
- Click Virus & Threat Protection.

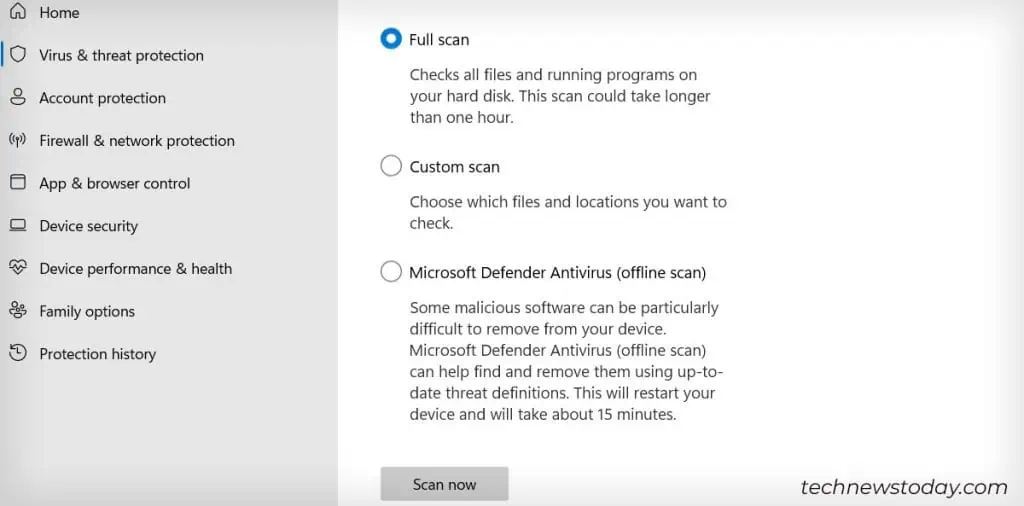
- Click Scan Options.
- Select Full Scan > Scan Now.

It might take a little time for your computer to finish scanning for viruses. Once it’s done, take any recommended actions and restart your computer to see whether the problem is fixed.
If you use a different antivirus, open the program and run a full scan.
Kill the Process Itself
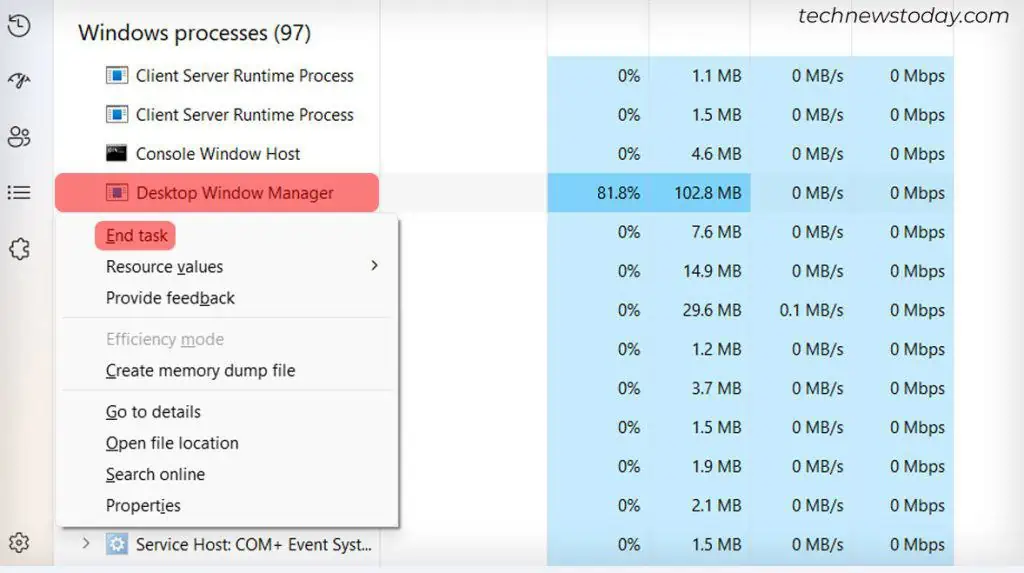
The dwm.exe process can also be stopped. Some users report a workaround where you can stop the process when you boot up the system and then may have a few hours without high CPU usage.
- Open Task Manager.
- Look for Desktop Window Manager under Windows Processes.
- Right-click Desktop Window Manager and click End Task.
- Select Abandon Unsaved Data and Shut Down.
- Click Shut Down.
If you are encountering high GPU usage due to Windows Desktop Manager, refer to our guide on Desktop Window Manager High GPU on Windows.