Windows 11 has introduced a number of new features and improvements, but one thing that remains unchanged is the process for accessing the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) on your computer.
The BIOS is a critical component of your system that is responsible for booting up your computer and ensuring that all of its hardware is functioning properly.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to access the BIOS and make any necessary changes to its settings on your windows 11 computer.
Using the BIOS key

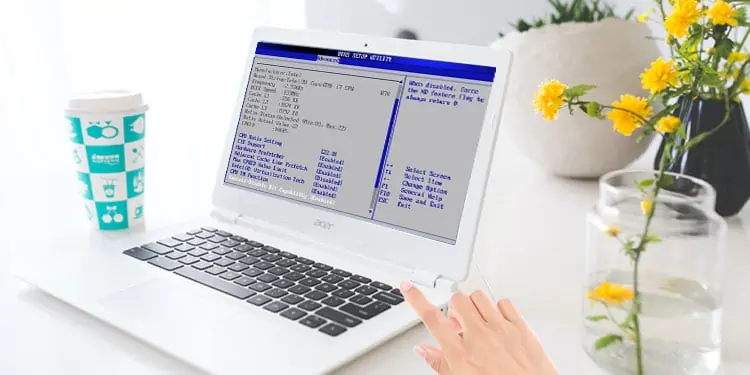
Depending on the different motherboards, the BIOS key can either be any of the function keys or the Delete key. If you do not know the key to enter the BIOS, search the internet for the BIOS key for your laptop or computer.
All you need to do is power on the computer and repeatedly press the BIOS key to get to BIOS. This method will work on any version of Windows. Below, we have mentioned the BIOS key for different motherboard manufacturers for PCs and laptops.
- HP: F10
- Lenovo: F2, F1 or Enter + F1
- Acer: F2 or Delete
- ASUS: F9, F10. or Delete
- Dell: F2 or F12
- MSI/Gigabyte/Zotac/BIOStar/EVGA: Delete
Advanced Startup
For Windows 10 and 11, you can also open Advanced Startup to access the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). Both UEFI and BIOS are similar. Both start before loading the OS. Most modern computers and laptops have the UEFI only instead of the BIOS.
In some laptops, you need to access the UEFI settings first before accessing the BIOS.
Follow the steps mentioned below to boot into Advanced Startup.
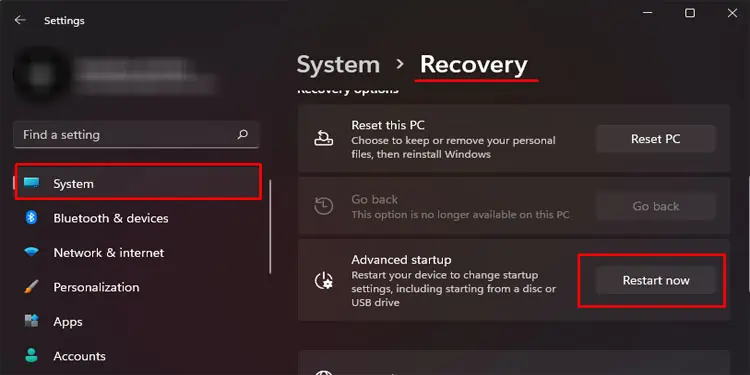
- Press the Windows + I key to open Settings
- Go to System > Recovery (Update & Security > Recovery for Windows 10)
- On Advanced startup, click on Restart now.

From Command Prompt
Below are the steps to boot into Advanced startup using the command prompt.
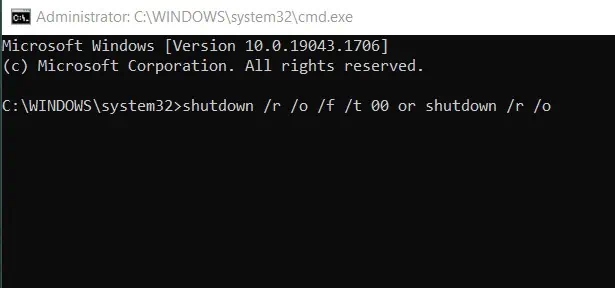
- Press the Windows + R key to open Run.
- Type cmd and press Enter.
- Now, type the following command and press Enter to boot into Advanced startup.
shutdown /r /o /f /t 00 or shutdown /r /o
From Shortcut
You can also access the Advanced startup using a shortcut.
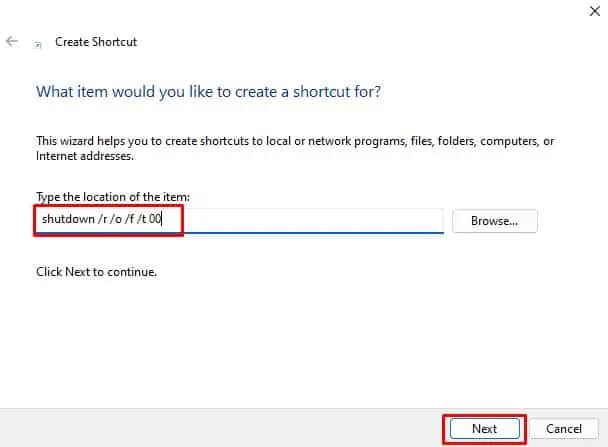
- Right-click on the desktop and click on New.
- Select Shortcut.
- Under Type, the location of the item, paste the following code and click Next
shutdown /r /o /f /t 00
- Click on Finish.
- Double click on the shortcut file you created to restart the PC in Advanced startup.
Alternatively, you can also press the Shift key when you click the restart button on the start menu to boot into the advanced startup directly.
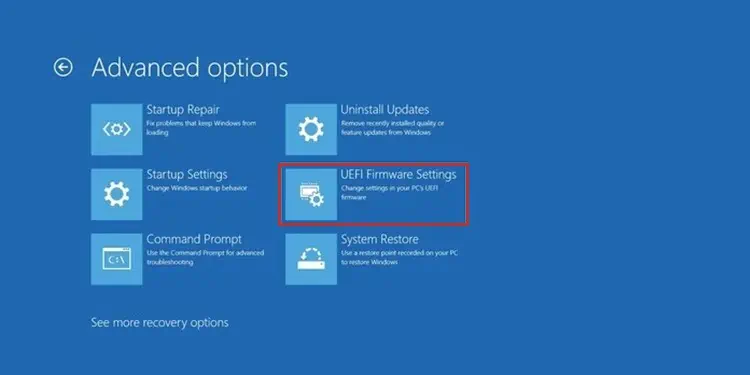
Once you are in the Advanced startup menu, follow the steps mentioned below to run the UEFI
- Click on Troubleshoot
- Select Advanced Options

- Select UEFI Firmware Settings
- Click on Restart to boot into UEFI (BIOS)