The Get-ADUser cmdlet is a very versatile tool that’s used to get active directory users. If you need to identify specific AD users, you can use values like their SAM account name to do so. Or you can use the Properties parameter when you need detailed info on one or more users.
Similarly, when you’re dealing with a large number of user objects, the Filter parameter is useful for getting AD users based on certain filters like Email, City, Title, etc. Combined with tools like sort and export, Get-ADUser makes user management in domains very convenient.
PowerShell Get-ADUser Requirements
On Domain Controllers, the Get-ADUser command obviously works by default. But if you try to run this command on other systems that are part of the AD domain, you may encounter the Get-ADUser is not recognized error.
This is because you must install the RSAT AD component first You can do so with Add-WindowsCapability –online –Name "Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0". Once you do this, you can use Get-ADUser on any system.
You won’t be limited to domain admin accounts either; any authorized AD user account will work. One thing to remember is that while non-admin accounts can retrieve most user object attributes using this command, some sensitive info might be accessible to domain admins only.
Get-ADUser Parameters
Get-ADUser primarily uses three parameters to retrieve user objects – Identify, Filter, and LDAPFilter.
Identity retrieves a user object using a specific value like its distinguished name or GUID. This is useful when you need to find a user object and remember the required value.
Filter returns a list of user objects based on the selected queries. In cases where you need to get AD users whose password has expired, or ones that haven’t logged in the last 2 weeks, and so on, filter can be useful. You can further narrow down the results to only user objects from specific servers, specific OUs, etc.
LDAPFilter also uses query strings to filter the user objects. The difference is that, unlike Filter which follows PowerShell syntax, LDAPFilter uses its own LDAP query syntax (attribute and value). This means it does have a slight learning curve, but you’ll find it to be a useful tool once you get used to it.
There are other useful parameters too like SearchBase and SearchScope that we’ll cover in our examples. We recommend referring to Microsoft’s documentation if you want to check the complete list of parameters, but the prior three are the ones we’ll focus on in this article.
Identity
Identity returns a single AD user object using one of the following properties:
- Distinguished name (DN)
- ObjectGUID
- objectSid (SID, or security identifier)
- SamAccountName
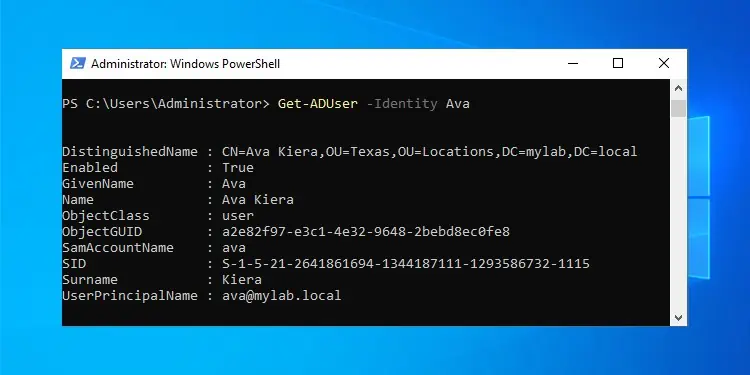
Let’s say you need details on a user named Ava. Assuming her SamAccountName is ava, you can retrieve the user object with Get-ADUser -Identity ava.
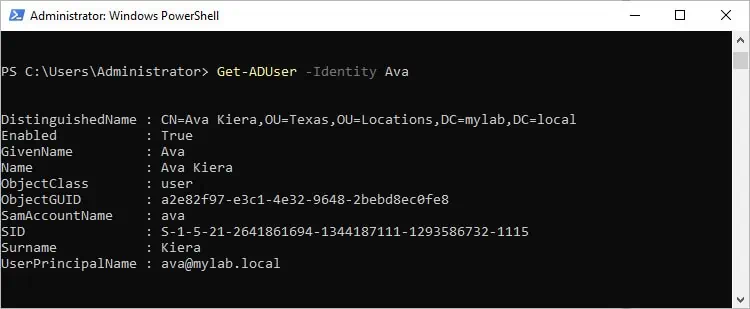
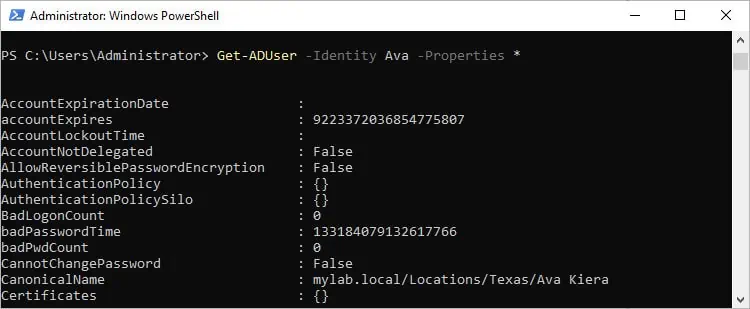
This command only returns 10 main properties though. If you need the complete properties list for a user object, you should use Get-ADUser -Identity ava -Properties * instead.
Filter
As people generally don’t remember the property values required for the Identity parameter, Filter tends to be more commonly used. Filter specifies a query string that follows the PowerShell Expression Language syntax to retrieve AD user objects. As such, the operator comes between the operand and the value.
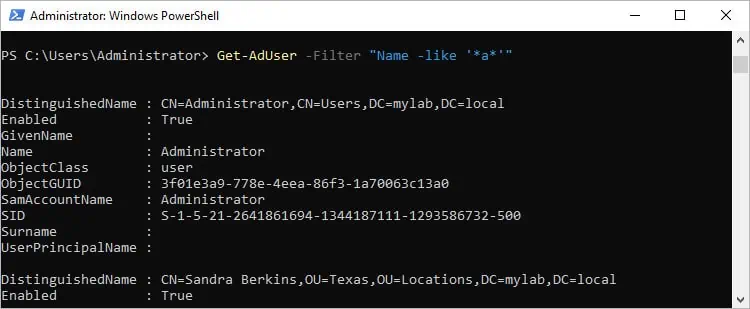
A basic example would be Get-AdUser -Filter "Name -like '*a*'", where Name is the operand, like is the operator, and a is the value. This command returns all user objects that contain the letter a in their name.
Another useful command is Get-ADUser -Filter * which retrieves all the AD objects.
Now, here’s the list of Filter operators:
| Operator | Function |
| eq | Equal to |
| ge | Greater than or equal to |
| le | Less than or equal to |
| ne | Not equal to |
| approx | Approximately equal to |
| gt | Greater than |
| lt | Less than |
| like | Like |
| notlike | Not like |
| and | All clauses must be true |
| or | Any of the clauses should be true |
| not | The clause must be false |
| band | Bitwise AND |
| bor | Bitwise OR |
As stated earlier, using Get-ADUser <user> -Properties * returns the complete list of properties. You can check this list for all the acceptable properties you can use to filter the output. But for now, here are some commonly used ones:
- AccountExpirationDate
- City
- Company
- Country
- CountryCode
- Department
- Description
- EmailAddress
- EmployeeID
- EmployeeNumber
- Enabled
- Initials
- LogonCount
- Name
- PasswordExpired
- SamAccountName
- State
- Title
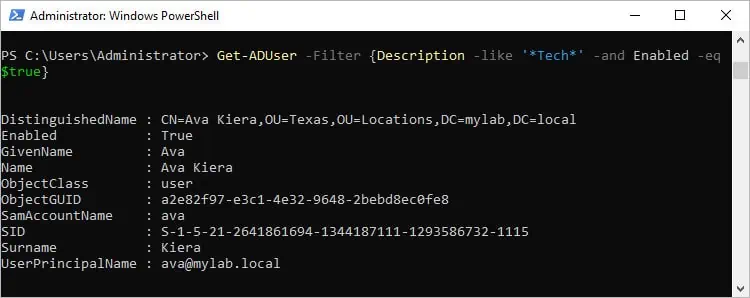
Using these operators and properties, you can create various types of filters. For instance, to only get users with Tech in their description, you could use Get-ADUser -Filter "Description -like 'Tech'". To list only active AD users, you’d use Get-ADUser -Filter 'Enabled -eq $true'
Similarly, you could combine the commands to list active AD users that have Tech in their description as such:Get-ADUser -Filter {Description -like 'Tech' -and Enabled -eq $true}
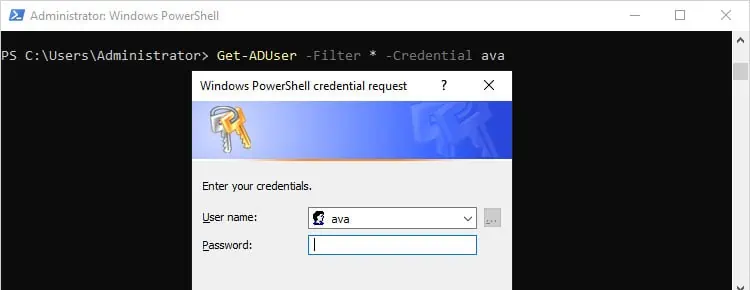
When on a non-admin account, you may encounter a non-terminating error if you don’t have permission to perform the task. In this case, you can use the Credential option to run the command with different credentials as such:Get-ADUser -Filter * -Credential ava
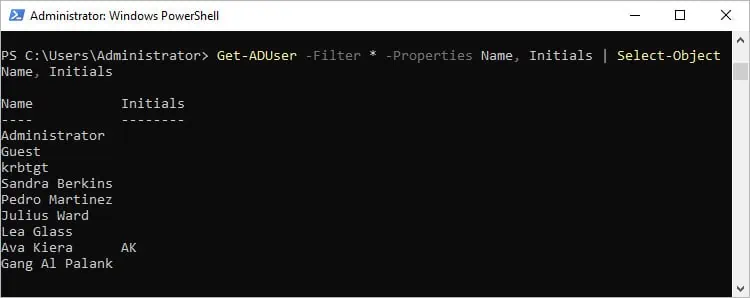
Finally, since Filter usually returns a lot of AD objects, you can further optimize the output by specifying the exact property values you need. Use the Properties parameter to retrieve the values first, then use the Select-Object option to display only the specified properties.Get-ADUser -Filter * -Properties Name, Initials | Select-Object Name, Initials
LDAPFilter
LDAP clauses follow the (ADAttribute Operator Value) format. Specifically, it uses the following operators:
| Operator | Function |
| = | Equal to |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| ~= | Approximately equal to |
| & | Boolean AND |
| | | Boolean OR |
| ! | Boolean NOT |
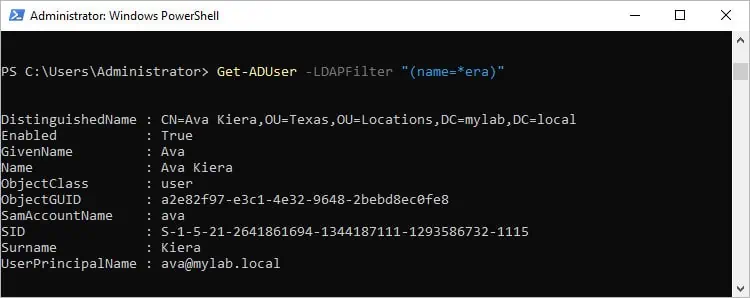
Let’s look at some basic examples. The following command returns AD objects whose names end with era:Get-ADUser -LDAPFilter "(name=*era)"
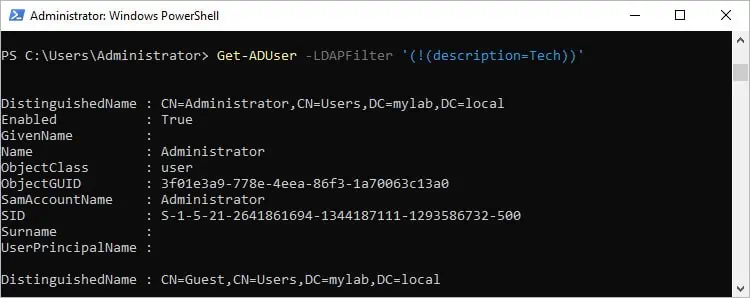
To get objects that don’t include Tech in their description:Get-ADUser -LDAPFilter '(!(description=Tech))'
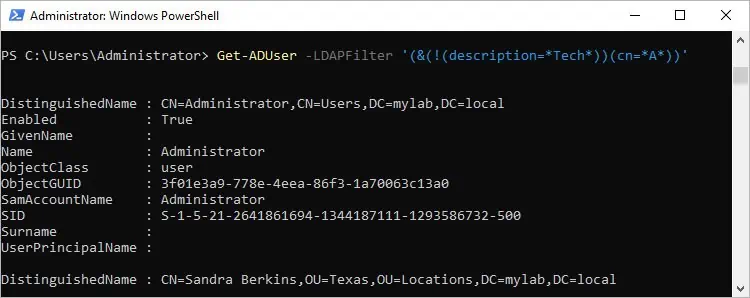
To combine multiple clauses so that you get objects with A in their name, but no Tech in the description:Get-ADUser -LDAPFilter '(&(!(description=Tech))(cn=A))'
Useful Get-ADUser Examples
You should have a handle on basic Get-ADUser usage at this point. We’ve listed more examples of some common use cases here that will demonstrate other useful parameters and scenarios.
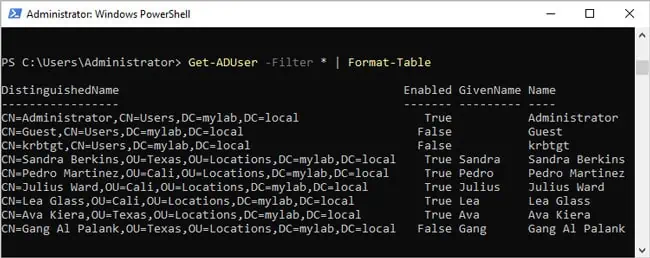
- To get the output in table format, use Format-Table or ft:
Get-ADUser -Filter * | Format-Table
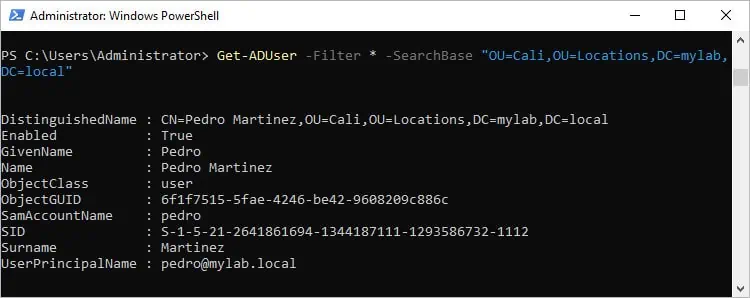
- To get objects from a specific container, use SearchBase:
Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=Cali,OU=Locations,DC=mylab,DC=local"
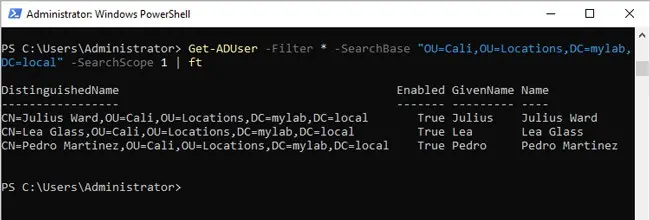
- To get objects down to a certain level of the OU hierarchy only, use SearchScope:
Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=Cali,OU=Locations,DC=mylab,DC=local" -SearchScope 1 | ft
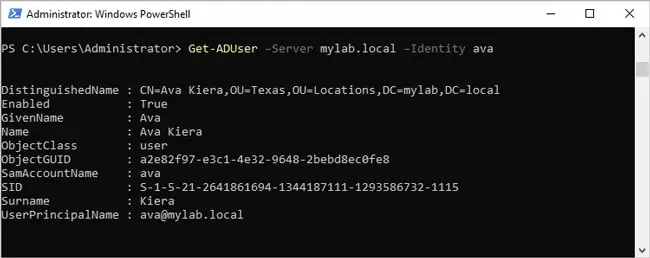
- To get objects from a specific domain controller, use Server:
Get-ADUser –Server mylab.local –Identity ava
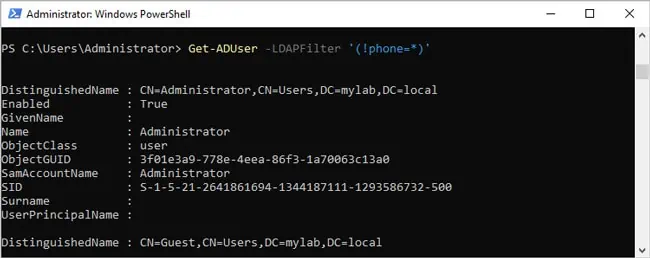
- To get users who don’t have a phone number set,
Get-ADUser -LDAPFilter '(!phone=*)'
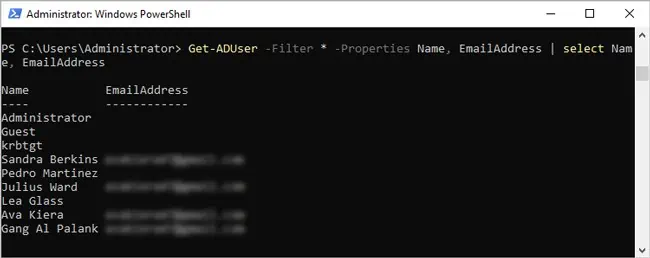
- To display the Email addresses of all users,
Get-ADUser -Filter * -Properties Name, EmailAddress | select Name, EmailAddress
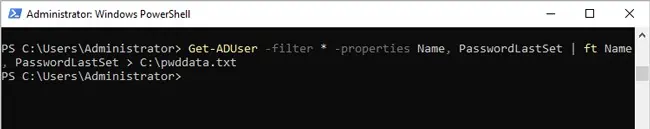
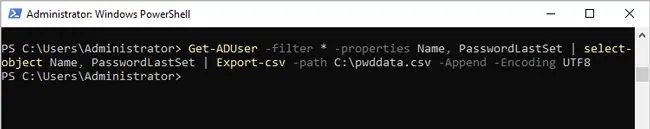
- To export the output to text,
Get-ADUser -filter * -properties Name, PasswordLastSet | ft Name, PasswordLastSet > C:\pwddata.txt
- To export the output to CSV,
Get-ADUser -filter * -properties Name, PasswordLastSet | select-object Name, PasswordLastSet | Export-csv -path C:\pwddata.csv -Append -Encoding UTF8