Gigabyte boards use different methods like audible beep codes, LED indicators, and Debug LED Codes to indicate different system states or errors. The first two methods are common, whereas the debug LED is only found on higher-end Gigabyte boards.
This LED (called the Debug Port or DB_PORT) displays hexadecimal codes like 55, D9, etc. If your motherboard is displaying such codes and not booting at the moment, you can use the code to diagnose and fix the problem.
This is easier said than done, though. A lot of the documented codes are described very vaguely. Speaking from personal experience, the manual was basically useless when diagnosing the debug code 25 on my TRX40 Aorus Master board.
So, I’ll cover the most common Gigabyte debug codes, what they mean, and how you can use this info to fix your actual problem in this article.
What Do the Gigabyte Debug Codes Mean?
Gigabyte boards can display over a hundred different codes, but most of these are harmless. About ⅔ of the codes simply indicate regular boot, S3 resume, and recovery states.
For instance, the board cycles through different codes during POST and eventually settles on A0. This just indicates that it successfully completed POST and has handed over control of the hardware to the OS.
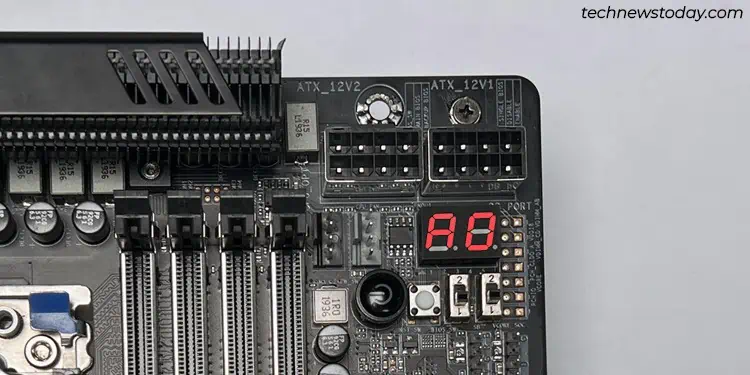
Or, you might see the E0 code after putting your system to sleep mode. This just indicates that the system is resuming from the S3 Sleep State.
I’ve seen a lot of users worried about such codes that are indicating normal system states. My point here is that you should check the code in the manual. If it’s not an error code, your system is likely working fine and there’s nothing to worry about.
Around ⅓ of the debug codes are indeed error codes, though. These are mostly fatal, meaning your system won’t boot until you diagnose and fix the problem. I’ll list them here according to Gigabyte’s documentation and then explain the troubleshooting process in the next section.
| Code | Description |
| 50~55 | Memory initialization error occurs. |
| 56 | Invalid CPU type or speed. |
| 57 | CPU mismatch. |
| 58 | CPU self test failed or possible CPU cache error. |
| 59 | CPU micro-code is not found or micro-code update is failed. |
| 5A | Internal CPU error. |
| 5B | Reset PPI is failed. |
| 5C~5F | Reserved. |
| D0 | CPU initialization error. |
| D1 | IOH initialization error. |
| D2 | PCH initialization error. |
| D3 | Some of the Architectural Protocols are not available. |
| D4 | PCI resource allocation error. Out of Resources. |
| D5 | No Space for Legacy Option ROM initialization. |
| D6 | No Console Output Devices are found. |
| D7 | No Console Input Devices are found. |
| D8 | It is an invalid password. |
| D9~DA | Can’t load Boot Option. |
| DB | Flash update is failed. |
| DC | Reset protocol is failed. |
| DE~DF | Reserved. |
| E8 | S3 resume is failed. |
| E9 | S3 Resume PPI is not found. |
| EA | S3 Resume Boot Script is invalid. |
| EB | S3 OS Wake call is failed. |
| EC~EF | Reserved. |
| F8 | Recovery PPI is invalid. |
| F9 | Recovery capsule is not found. |
| FA | Invalid recovery capsule. |
| FB~FF | Reserved. |
Note: If you’re facing a Reserved error code, you’ll either need to reach out to Gigabyte or check out online forums to figure out what that exact code indicates.
For instance, my board was displaying the 25 debug code a while back. This is only marked as Reserved in this manual.
I had to figure out myself that there was a conflict for the RAM’s LED control between Gigabyte’s RGB Fusion 2.0 and iCUE. Eventually, I uninstalled the Gigabyte App Center, which fixed the issue.
Troubleshooting Using Gigabyte Debug Codes
Once you identify the faulty component through the code, you can follow the troubleshooting steps from the appropriate section.
Fixing RAM Issues
RAM issues mostly come down to faulty hardware (i.e., defective slots or modules). This makes troubleshooting it fairly straightforward. Try each step and move on to the next if it doesn’t help:
- First, simply reseat the RAM sticks. When reinstalling them, make sure to orient them correctly and insert them fully such that the latches lock in place. You can also clean the RAM slots or sticks if required.

- Remove the sticks. Grab one of them and try it on all the slots one by one. Repeat the same for any other sticks.

- If possible, you can even test the sticks on another system. Eventually, you should be able to narrow down the faulty component to the RAM sticks or the slots.
Troubleshooting the CPU
CPU-related error codes usually indicate bent CPU pins or power supply issues. In the worst case, you could also be dealing with a dead processor or defective socket/motherboard.
- First, try booting without the CMOS battery. This should reset the BIOS to defaults and resolve any CPU voltage issues.

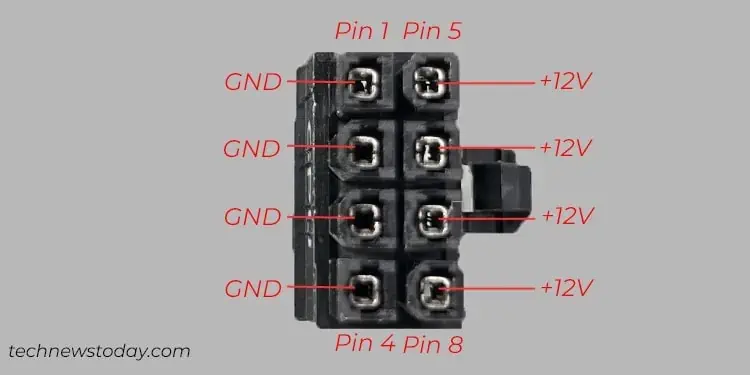
- Next, reseat all the power connections. You could even directly test the CPU power connector with a multimeter to ensure it’s receiving enough voltage.

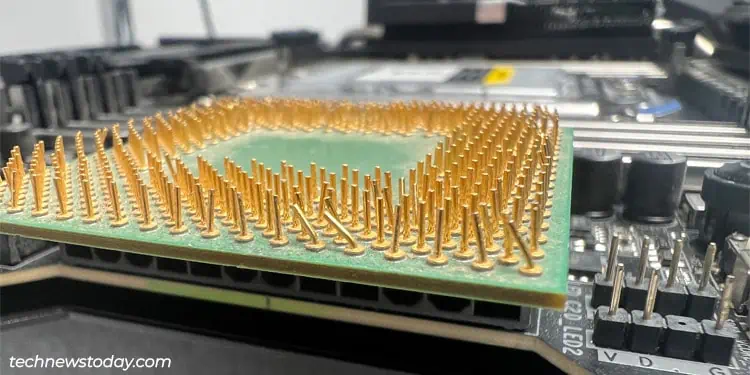
- Carefully remove the CPU cooler, and then the CPU. Check if any of the pins are bent. It’s usually possible to repair a few bent pins, but if a lot of them are damaged, you may need to replace the CPU.

- If possible, you could also test the CPU on another system. This should help you determine whether the CPU or the socket is defective.
Troubleshooting the Motherboard Components
Your Gigabyte board has a lot of possibly defective components from the BIOS chip and CMOS ROM to the PCIe, SATA and USB slots. To troubleshoot these,
- I recommend that you start by booting without the CMOS battery like earlier. This will resolve any misconfigured BIOS settings related to boot devices, BIOS passwords, unstable overclocks, etc.
- If you’re using an older BIOS version, updating the BIOS is likely to fix any compatibility issues with PCIe and USB devices.
- On the hardware-end, you could remove all PCIe and USB devices and only boot the board with the bare minimum. This can help identify any defective peripherals.
- Reinstall the devices one by one. Do so properly and test the boot process after adding each one.
- The troubleshooting process from earlier can also be useful here (try the devices on different slots, or on a different system).
- Finally, for display issues specifically, remember to try different display cables too (e.g., DP instead of HDMI this time).
What If The Problem Persists
I’m repeating myself here but that’s because these steps are just that important/effective. Make sure you at least try these before moving further:
- Remove the CMOS battery to reset the BIOS.
- Update your Gigabyte BIOS version.
- Reseat the RAM modules, or replace them if required.
At this point, the motherboard itself may be defective. In this case, there’s not much most users can do.
I recommend reaching out to Gigabyte support or taking your system to a local repair professional. They will advise you on whichever component is the problem and whether you can get it repaired/replaced.